Silver Recovery from Fixer Solutions through Metallic Replacement: A Sustainable Approach to Resource Conservation
Within the ever-evolving narrative of environmental responsibility and resource mindfulness, a crucial chapter emerges – the conscientious management of photographic waste. In this chapter, a tale of great significance unfolds, one that spotlights the handling of photographic waste as a key consideration. Amidst this tale lies a concealed treasure – silver, a precious metal often obscured within the depths of used photographic fixer solutions. These unassuming solutions, pivotal to the world of film and photo paper development, harbor a latent promise: the presence of silver ions. Through the deft and meticulous practice of metallic replacement, we embark on a journey that not only champions waste reduction but also resonates with a profound call to safeguard our invaluable resources.
( to buy the Silver Trap Window on e-bay press TRAP)
The Significance of Silver Recovery
Silver, a highly valued metal with applications spanning photography, electronics, and jewelry sectors, occupies a pivotal role in the intricate process of image formation on both film and paper mediums. However, as photographic materials undergo processing, they release silver ions into fixer solutions. If not managed properly, these ions can trigger environmental contamination. Through the adoption of silver retrieval methodologies, specifically the sophisticated practice of metallic replacement, the invaluable silver content can be harnessed and reused, all while concomitantly mitigating the far-reaching repercussions on the environment.
Metallic Replacement Process
The methodology of metallic replacement stands as an artful and scientifically grounded approach for the retrieval of silver ions from fixer solutions. This intricately choreographed process capitalizes on the inherent reactivity exhibited by select metals like steel or aluminum, thoughtfully chosen to supplant silver ions residing within the solution. Through this calculated interplay, silver ions undergo a transformative journey, culminating in their reduction and firm adherence to the awaiting surface of the chosen metal. This metamorphosis results in the creation of a tangible stratum of solid silver, a tangible testament to the method’s prowess.
Beyond the captivating science, this process unfolds with a pragmatic elegance, simultaneously addressing the dual challenges of resource conservation and waste management. However, in the realm of practical application, certain considerations can significantly enhance its efficacy. Primarily, the choice of reactive metal plays a pivotal role; selecting one with an optimal balance of reactivity and practicality can yield heightened results. Additionally, the monitoring of reaction parameters, such as temperature and solution concentration, demands meticulous attention to ensure the desired outcomes.
Furthermore, seamless integration of this method into existing waste management frameworks is key. Collaborating with specialized facilities for further silver extraction and refinement is a prudent step. Such collaboration not only ensures optimal recovery but also adheres to regulatory standards, promoting a comprehensive and compliant approach.
In essence, the metallic replacement process is a testament to the synergy of science and practicality, offering a profound avenue for both environmental stewardship and resource optimization. By weaving scientific precision with strategic decision-making, its potential can be fully harnessed, underpinning a holistic approach towards a sustainable future.
Steps of Metallic Replacement
- Collection of Fixer Solutions: The initial phase involves the collection of used fixer solutions from photographic processing facilities. These solutions contain a blend of silver ions, chemicals, and impurities.
- Preparation of Reactive Metal: A reactive metal, often in the form of steel wool or aluminum shavings, is meticulously prepared. This metal’s high reactivity serves as the catalyst for reducing silver ions within the fixer solution.
- Metallic Replacement Reaction: The reactive metal is introduced into the fixer solution. As the two components interact, silver ions undergo reduction, clustering onto the surface of the reactive metal. This dynamic process culminates in the creation of a solid silver layer.
- Solid Silver Separation: Once the metallic replacement reaction has run its course, the amalgam of solid silver-coated reactive metal is separated from the solution. This composite material undergoes subsequent processing stages to extract the solid silver.
- Refining the Recovered Silver: The retrieved solid silver undergoes refining procedures to eliminate any impurities. The refined silver subsequently enters the realm of melting and refinement. The resultant pure silver can be either sold or reincorporated into diverse applications, alleviating the demand for freshly mined silver.
Benefits of Metallic Replacement
- Environmental Impact: The practice of silver recovery via metallic replacement demonstrates a keen commitment to minimizing the release of silver ions into the environment. This proactive stance mitigates the potential for water contamination and environmental harm.
- Resource Conservation: The adoption of metallic replacement assumes the role of a resource conservation advocate. By recovering silver from fixer solutions, the demand for fresh silver extraction is mitigated, thereby alleviating the ecological impact associated with mining activities.
- Cost Efficiency: Metallic replacement embodies an economically viable approach to silver recovery. The process proves to be financially prudent when juxtaposed with the costs associated with procuring new silver for industrial applications.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions have instituted regulations governing the proper disposal of photographic waste. The adoption of metallic replacement aligns with these regulations, fostering compliance and circumventing potential penalties.
Exploring this intricate metallic replacement process isn’t just a rundown of steps; it’s a peek into the services we offer, thanks to our years of expertise in recovering precious metals. As part of our commitment to sharing knowledge transparently, we’ve captured the various stages of this process through detailed images. These visuals take you on a journey, from collecting the solution to preparing the reactive metal, showcasing the dance between the elements, and culminating in the separation of solid silver. We’re firm believers that this immersive insight not only showcases our capabilities but also empowers others on their journey toward sustainable resource management.
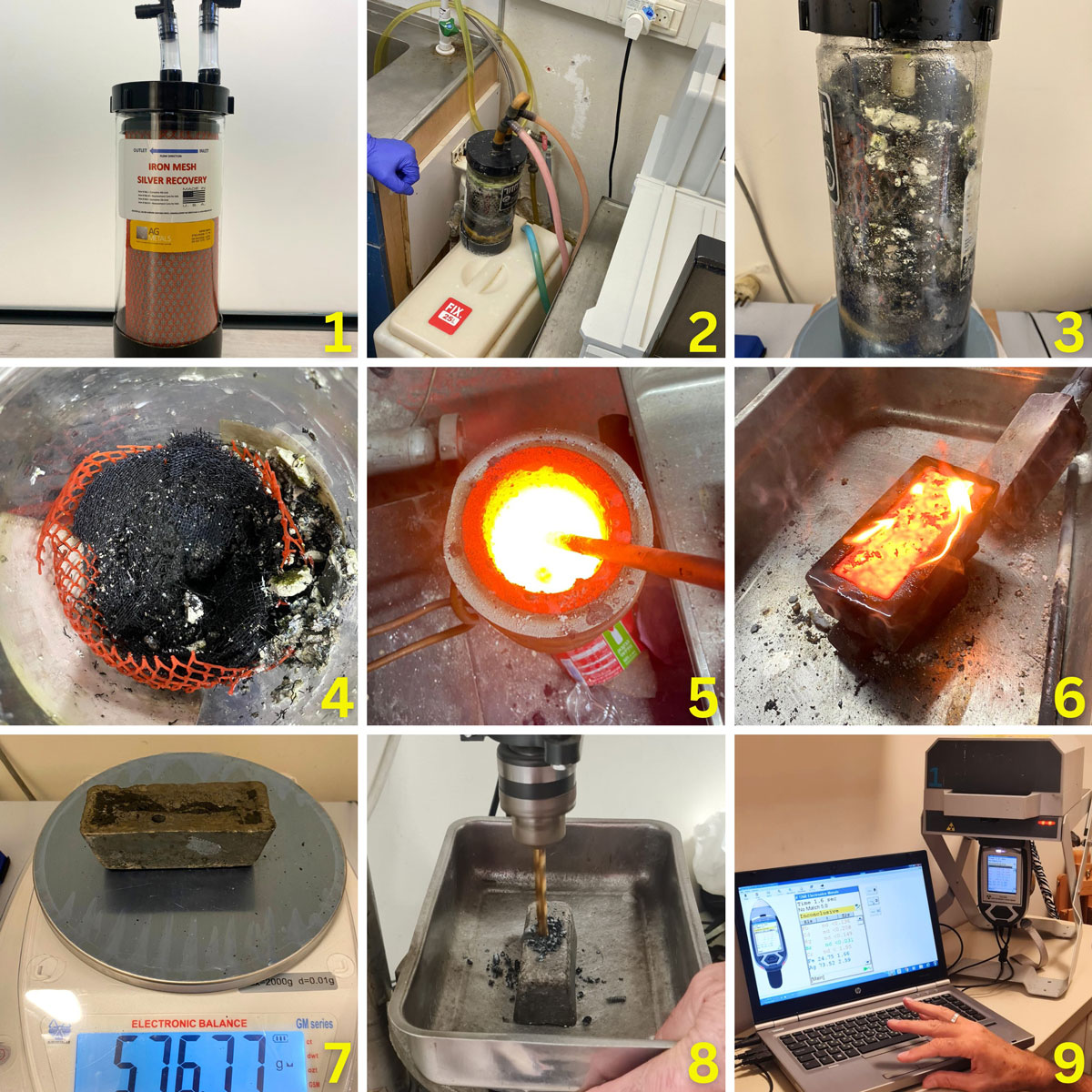
In the image series below, we share the stages of recovering silver from a used Silver Trap Windows cartridge filter.
- Image 1: New Silver Trap Windows cartridge filter.
- Image 2: Filter installed at an X-ray film development station
- Image 3: Used filter with visible deposits
- Image 4: Deposits from filter after washing out excess fixer and drying
- Image 5: Casting in an induction furnace
- Image 6: Pouring and molding of molten metals
- Image 7: Weighing the cooled bar
- Image 8: Drilling and collecting pieces of metal bar
- Image 9: XRF Analysis to determine metal composition

In the captivating world of photographic waste, a treasure hunt for silver is underway, leading us to a remarkable solution – metallic replacement. This method not only salvages silver from used fixer solutions but also stands as a beacon of responsible waste management and resource stewardship.
Silver’s multifaceted significance in industries spanning from photography to electronics is matched by the environmental challenges it poses when not managed effectively. Enter metallic replacement – a process that elegantly transmutes silver ions into a tangible asset, safeguarding our planet from potential contamination.
Through strategic stages, from solution collection to refining the recovered silver, metallic replacement showcases its prowess. It doesn’t just recycle silver; it pioneers a sustainable mindset that aligns industry demands with ecological sensitivity.
The advantages are manifold – from environmental prudence and resource conservation to cost-effectiveness and regulatory compliance. This journey underscores the potential for industries to not only flourish but also champion environmental responsibility.
As technology propels us into the future, metallic replacement serves as a roadmap for sustainable progress. In a world striving for harmony between industrial might and environmental mindfulness, this process shines as an embodiment of balance, innovation, and silver’s enduring brilliance.